Top 10 Sound Absorption Materials for Effective Noise Control
In today’s noisy world, effective noise control is essential for comfort and productivity. Sound absorption materials play a crucial role in reducing unwanted sound. These materials can transform a space into a more serene environment.
Various sound absorption options exist, each with unique properties and applications. For instance, acoustic panels are popular in offices and studios. They help minimize echo and enhance clarity. Other materials, like carpets and curtains, are also effective but may not offer the same level of absorption.
The effectiveness of sound absorption can vary widely. Some solutions may not meet the specific needs of a space. Choosing the right material requires careful consideration of the environment. Understanding these options is key to creating a quieter, more enjoyable experience. In this article, we will explore the top 10 sound absorption materials available today.
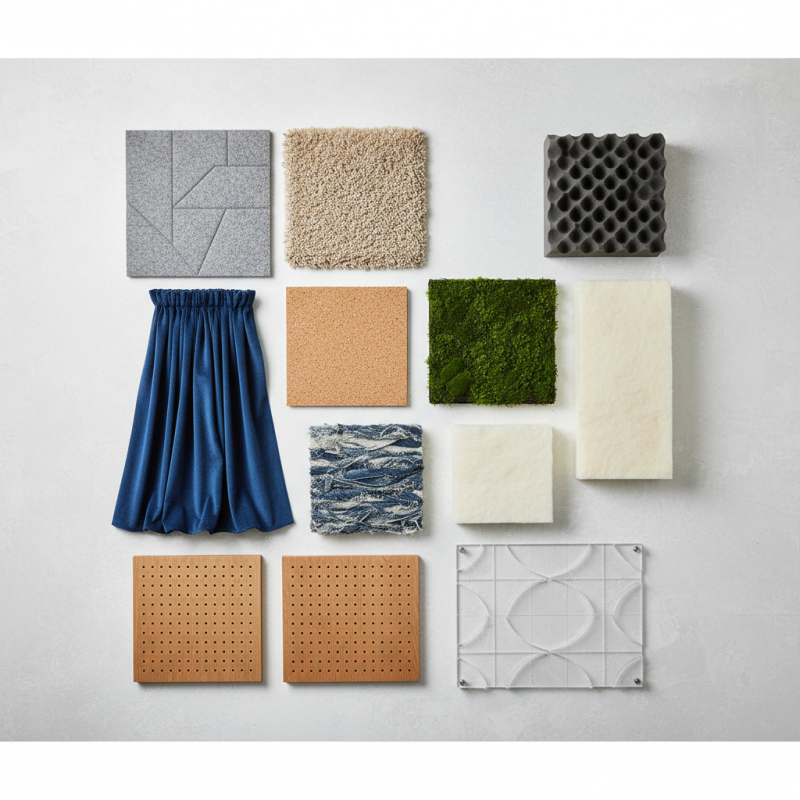

Overview of Sound Absorption and Its Importance in Noise Control
Sound absorption plays a crucial role in noise control. It helps reduce unwanted sounds in various environments. This is especially important in places like offices, schools, and hospitals. Excessive noise can cause stress, distraction, and even health issues.
Effective sound absorption materials can significantly enhance the acoustic quality of a space. Soft fabrics, foam panels, and carpets are common choices. They trap sound waves and prevent them from bouncing off hard surfaces. However, not all materials work equally well. Some might not provide sufficient absorption in specific frequency ranges.
Choosing the right material can be overwhelming. Each environment has distinct acoustic challenges. What works in a home theater may not suit an open office. Sometimes, people overlook the importance of proper installation, which can hinder performance. Therefore, understanding the specific needs is vital for effective noise control.
Common Applications of Sound Absorption Materials in Various Industries
Sound absorption materials play a vital role in multiple industries. They minimize noise and improve sound quality. In offices, overly loud environments can undermine productivity. A study by the International Institute of Noise Control Engineering found that effective sound absorption can enhance concentration by 30%.
In the hospitality industry, reducing noise is critical. Hotels utilize sound-absorbing panels to create tranquil spaces. Research shows that quiet rooms significantly increase guest satisfaction. Hotels that prioritize sound control report a 20% increase in positive reviews. Areas like restaurants benefit too; sound-absorbing materials often lead to a 15% rise in customer retention.
Manufacturing facilities face unique challenges. Excessive noise can violate safety regulations. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, excessive sound levels are harmful. Using sound absorption materials not only protects employees but also complies with legal standards. Despite these benefits, many factories still overlook this issue. They risk both health and productivity.
Top Natural Materials for Sound Absorption: Features and Benefits

Natural materials play a crucial role in sound absorption. Many architects and designers prefer these options for their effective noise control properties. Acoustic panels made from natural fibers, like wool and hemp, can reduce noise levels significantly. Studies show that natural materials can absorb up to 90% of sound energy in certain conditions, making them ideal for busy environments.
Wood is another excellent choice for sound absorption. It offers a warm aesthetic alongside effective acoustic performance. Research indicates that specific wood varieties can reduce reverberation times by up to 30%. Traditional materials often lack the charm that natural options provide. Some options, however, can be hard to source. Sustainability is essential; otherwise, the ecological impact cancels out the benefits.
Cork, a lesser-known alternative, has superb sound-absorbing properties. It can attenuate sound frequencies and is lightweight. Reports suggest that cork can lower noise levels by around 50% in small spaces. While many consumers overlook it, cork deserves attention. Its unique texture adds character, yet its availability may be inconsistent. This situation calls for reflection on sourcing practices.
Synthetic Sound Absorption Materials: Types and Performance Analysis
When it comes to noise control, synthetic sound absorption materials play a crucial role. Various types of these materials have emerged, each with distinct properties and applications. For example, polyurethane foams are popular for their lightweight structure and high efficiency. Studies indicate they can reduce echo in rooms by up to 85%, making spaces more comfortable for conversations and meetings.
Another noteworthy option is polyester fibers. These are often used in office environments to dampen noise. Data shows that they can absorb sound frequencies effectively between 500 Hz and 2000 Hz. This range is particularly critical for human speech, suggesting their usefulness in busy workplaces. They also offer fire resistance, which adds a layer of safety to their soundproofing capabilities.
Despite their benefits, one must consider the limitations of synthetic materials. For instance, some may degrade over time, losing their effectiveness. Additionally, environmental concerns arise from the production and disposal of these materials. As we seek to maximize efficiency, a balance between performance and sustainability is necessary. Understanding the nuances of each material ensures better decision-making when implementing noise control solutions.
Innovative Advances in Sound Absorption Technologies for Future Use
Innovative sound absorption technologies are changing how we manage noise in various environments. Advanced materials are being utilized in architecture, automotive design, and industrial settings. These materials work effectively to minimize sound reflections and vibrations. They help create quieter spaces that enhance comfort and productivity.
Recent innovations include the use of biodegradable options. Such materials are eco-friendly and offer promising absorption capabilities. Additionally, flexible barriers and panels are gaining traction. They can be easily installed in diverse settings, offering acoustic solutions without compromising aesthetics.
Despite the progress, challenges remain. Some new materials may not perform as expected in different environments. Manufacturers are exploring various compositions to find the right balance between cost and functionality. Continuous research is necessary to fully realize the potential of these technologies. With the right focus, effective noise control could be more accessible in the near future.
Top 10 Sound Absorption Materials for Effective Noise Control
| Material | Sound Absorption Coefficient (α) | Frequency Range (Hz) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Foam | 0.75 - 0.90 | 250 - 2000 | Studios, Home Theatres |
| Mineral Wool | 0.80 - 1.00 | 500 - 4000 | Commercial Buildings, HVAC |
| Mass Loaded Vinyl | 0.70 - 0.85 | 125 - 4000 | Walls, Ceilings |
| Carpet Tiles | 0.30 - 0.45 | 125 - 2000 | Offices, Residential Spaces |
| Sound Absorbing Panels | 0.70 - 0.95 | 500 - 5000 | Auditoriums, Theatres |
| Fiberglass Panels | 0.90 - 1.00 | 250 - 4000 | Industrial Applications |
| Wood Wool Panels | 0.70 - 0.85 | 125 - 3000 | Cafés, Restaurants |
| Cotton Acoustic Panels | 0.50 - 0.75 | 300 - 3500 | Home Offices, Studios |
| Earth Wool Batts | 0.60 - 0.80 | 125 - 2000 | Passive House Construction |
| Recycled Paper Composite | 0.55 - 0.70 | 250 - 3000 | Sustainable Design Projects |
Related Posts
-
Why Soundproof Foam is Essential for Better Home Acoustics and Noise Control
-

Top 10 Advantages of Using Acoustic Foam for Soundproofing Your Space?
-

How Sound Dampening Improves Home Comfort and Productivity
-

Creating Your Perfect Soundproof Room for Ultimate Peace and Quiet
-

Unlocking the Secrets of Sound Dampening Techniques for a Quieter Home Environment
-

Exploring Innovative Sound Deadening Panels at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025